Digit Memory Span
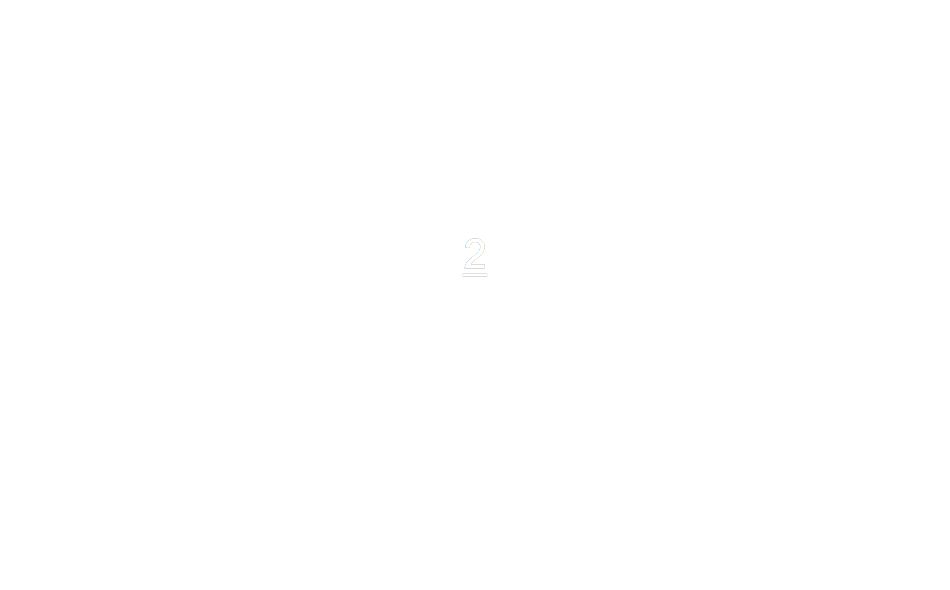
The limitation of working memory to hold discrete units to an amount of 7 ± 2 items is called memory span and is a well proven finding in the field of cognitive research. The digit memory span test measure how many digits a subject can reproduce from a series of digits presented to them. The length of the series is increased with each correct reproduction. The test is aborted when the subject failed to reproduce two consecutive sequences. The length of the last correctly reproduced sequence is the estimate of the memory span. If the reproduction should be in reverse order, the executive control function is more prominent since the items must be re-ordered.
This task is relying heavily on an articulatory control process which is used for verbal rehearsal which was traditionally considered as the short term memory. In contemporary models of the working memory, there is also visuo-spatial sketch pad which handles non-symbolic information such as images and spatial information.
The drastic limitation of short term memory compared to the vast capacity of long term memory has led to a ”bottleneck” model of human memory, where any information must pass the narrow working memory before it is either forgotten or stored in long term memory.
Publications
Baddeley, A. D., & Hitch, G. (1974). Working memory. In K.W. Spence and J. T. Spence (eds.) The Psychology of Learning and Motivation, vol 8. (pp. 67-89). New York: Academic Press.
Miller G A (1958) The magical number seven, plus or minus two: Some limits on our capacity for processing information. Psychological Review 63:81-97
Shiffrin R M (1975) Short term store: the basis for a memory system. In: Restle F (Ed) Cognitive Theory I. Hillsdale, Erlbaum
Links
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Baddeley’s_model_of_working_memory
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Magical_Number_Seven,_Plus_or_Minus_Two
Configuration Options
| Task Mode | : | Original Order| Reverse Order |
| Start Length | : | Number of digits in search set (default 2) |
| Stop Rule | : | Number of consecutive errors |
